CDsza
Hair Transplant
Hair transplants techniques have improved dramatically in the past few years. Advances in FUE techniques provide us the tools to deliver natural results that were not available before.

Dr. Marissa Milchak – Director of Hair Medicine and Hair Transplant

Dr. Marissa Milchak is the Director of Hair Medicine and Hair Transplant at Ringpfeil Advanced Dermatology.
Seeing over 700 hair loss patients each year, Dr. Milchak and her team deliver the most advanced medical and surgical hair restoration treatments available today.
Dr. Milchak is a fellow of the American Academy of Dermatology and a member of the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery.
Dr. Milchak sees Hair Restoration patients at both our Main Line and Philadelphia Center City offices.

FUE Hair Transplant
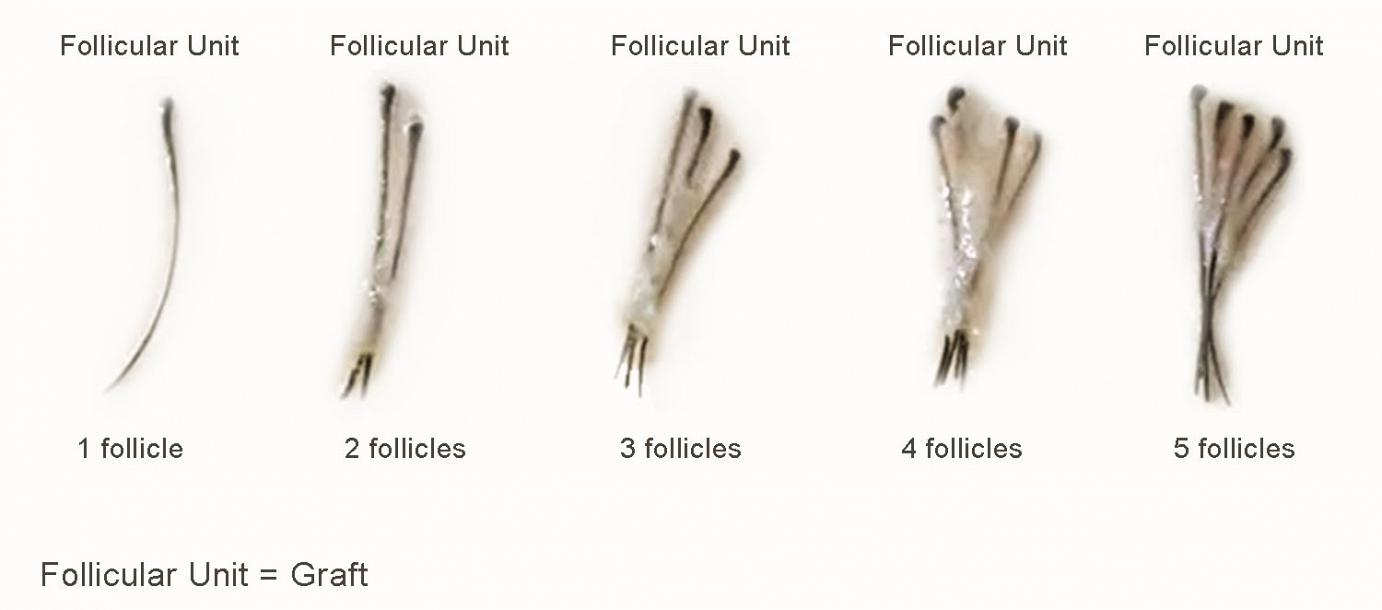
FUE – Follicular Unit Extraction – is a relatively newer technique in which the surgeon takes individual hair folilcles from a donor area and plug them accurately in the target area. The donor area are usually located in the back of the head where most people have denser hair.
Follicular Units
FUE – Follicular Unit Extraction – is a relatively newer technique in which the surgeon takes individual hair folilcles from a donor area and plug them accurately in the target area. The donor area are usually located in the back of the head where most people have denser hair.

FUT (Strip) Hair Transplant
FUT Hair Transplant was the first big leap forward in hair transplant in recent years. Here, a strip of skin is cut from the donor area (usually the back of the head, where hair is usually denser). The extracted strip is then dissected and single follicles are separated and prepared for implantation in the target area. The open edges of the donor area are then pulled towards each other and sewn together creating a nerrow scar that is later covered by the hair.
FUT – Follicle Harvesting Steps
- The number of follicles needed is calculated
- Density in donor area is measured, and strip location and dimension is determined
- Strip area is marked and shaved
- Local anathetic is applied to the area
- Dr. makes the incision to remove the the strip
- The Dr. sutures and close the skin
- Technicians separate the follicles from the strip and store them in holding solution
FUE VS. FUT
FUE & FUT – different in harvesting but similar in implantation
| advantage | FUE | FUT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FUT | Graft survival rate | Lower (85%) | Higher (95%) |
| FUT | Shaving donor area needed | yes | no |
| FUT | # grafts from "safest" donor area | Smaller | Larger |
| FUT | #grafts / day | Smaller (up to ~2500) | Larger (up to ~3500) |
| FUE | Scaring in donor area - shape | Dot-like | Linear |
| FUE | Scaring - Hiding by | Short hair | Long hair |
| FUE | Recovery time | Shorter (a day or two) | Longer (two days or more) |
| FUE | Invasive procedure | No | Yes |
| FUE | Donor area size | Broader | Limited |
| Similar | # of lifetime grafts | ~6000 | ~6000 |
| Similar | Target area natural look | Yes | Yes |
Facial Hair Transplant
We see a very strong demand for beard transplant. While the transplant to this area raises some chanllanges, the patient satisfaction for that procedure is extremely high.
The donor area can be hair from an area between the neck and the chin, but in most cases this area can not supply enough grafts satisfy the desired results. In most cases, most of the hair will be harvested from the occipital scalp (back of the head).
The visible location of the implantation calls for very accurate and artistic implantation. Wrong insertion angles and inconsistant density becomes very visible. The facial hair consists of single and double follicular units that needs to get out of the surface in a 10-20 degree angle.
Most of our patients who are interested in this procedure are 25-35 young man who are looking to increase hair density and hair uniformity. Some patients are interested to enhance specific facial areas such as the sideburn, cheek, or chin.
Hair loss causes and treatments
| Forms of hair loss | Cause | Treatments |
|---|---|---|
| androgenetic alopecia | male/female pattern hair thinning hormones, genetics | topical/oral minoxidil finasteride spironolactone PRP( platelet rich plasma) hair transplant |
| alopecia areata | autoimmune condition in which the body attacks hair follicles | topical therapies steroid injections light therapy systemic immunosuppressants |
| telogen effluvium | "stress" hair loss, illnesses, childbirth, surgeries, rapid weight loss, emotional/mental distress | time- usually reverses topical minoxidil PRP |
| trichotillomania | habitual hair pulling can be associated with OCD or other psychiatric conditions | habit-reversal therapy antidepressants N-acetylcysteine PRP hair transplant (after pulling stops) |
| traction alopecia | habitual hair pulling can be associated with OCD or other psychiatric conditions | loose hairstyles topical therapies steroid injections hair transplant (after pulling stops) |
| lichen planopilaris (LPP) frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) | inflammation attacking hair follicles | topical therapies steroid injections finasteride light therapy systemic immunosuppressants |
| central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA) | unknown- genetics? chemicals/heat? | topical therapies oral antibiotics antimalarials steroid injections PRP hair transplant |
Male Baldness Pattern – Norwood Classification System
Donor Area
The Norwood Class VII depicts the relatively safer donor area. When planing the harvesting the surgeon applies considerations such as
- Hair density
- Hair caliber
- Hair pigment
- Changes in hair properties as patient ages
- Root cause for hair loss
- Hormones stability
- Reserves for future treatments